The Top menu provides access to the sequence browser and to other interfaces through which the fasta manager tasks can be executed. This allows the user to process and analyze all the sequences included in one or multiple fasta files simultaneously without the need of open the files separately.

Figure 2: Main menu of the SeqEditor Application
TOP MENU: DIRECTORY
[ Directory → Select directory folder ]: to select the root folder shown in the Directory Browser.[ Directory → Show ]: view the Directory Browser.[ Directory → Hide ]: hide the Directory Browser.TOP MENU: FILE
[ File → New ]: To create a new nucleotide or protein sequence file.[ File → Open file ]: To open a sequence file.[ File → Save ]: To save current active file.[ File → Save as ]: To save the current active file as new file.[ File → Save All ]: To save all opened file in SeqEditor.[ File → Close ]: To close the current active file.[ File → Save All ]: To close all opened file in SeqEditor.TOP MENU: SEQUENCES
[ Sequences → Orientation and geometry ]
[ Orientation and geometry → change seq orientation in fasta files ]: Changes the orientation of the sequences in one or more fasta files by selecting Reverse, Complement or Reverse complement option.[ Orientation and geometry → change seq geometry in fasta files ] : Changes the geometry of the sequences in one or more fasta files by selecting either DNA or RNA.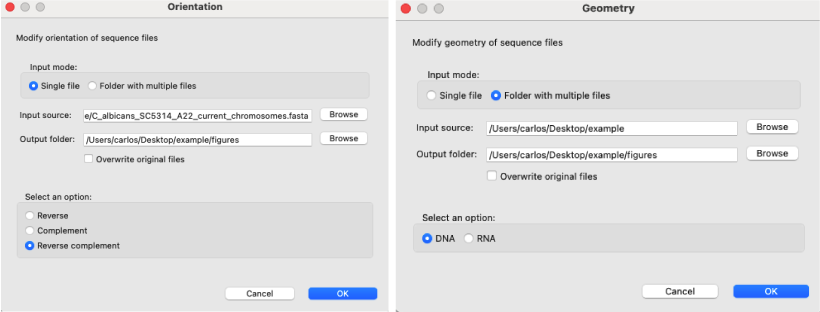
Figure 3: Orientation and Geometry windows layout. Left) The orientation dialog allows the user to change the orientation of the sequences to their reverse, complement or reverse complement sequences; Right) The geometry dialog allows the user to change sequences from DNA to RNA or vice versa.
[ Filter and sort → Filter sequences in fasta files ]: Filters sequences in fasta files using search terms provided in either a list of terms or a CSV file, selecting a matching criterion: Exact match, Partial match or Regular expression.
[ Filter and sort → Sort sequences in fasta files ]: Sorts sequences in fasta files using either an alphanumeric criterion or in a forced manner by giving search terms contained in a CSV file.
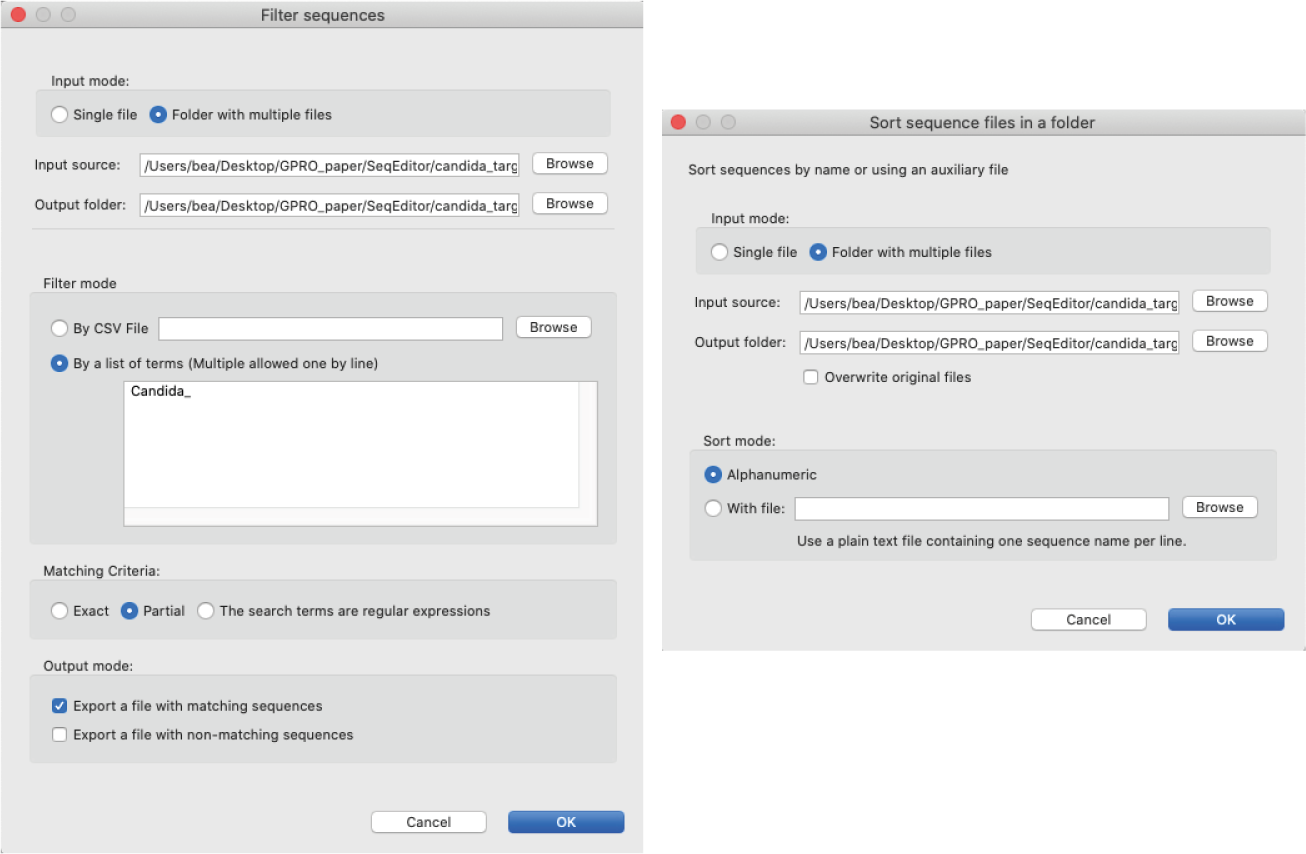
Figure 4: Filter and Sort windows. Left) The ”filter” dialog allows the user to filter sequences by given search terms and matching criteria; Right) The ”sort” dialog allows the user to sort sequences either alphanumerically or by a given term in a CSV file.
[ Sequences → Split sequences ]:To split sequences of a given file according to different criteria.
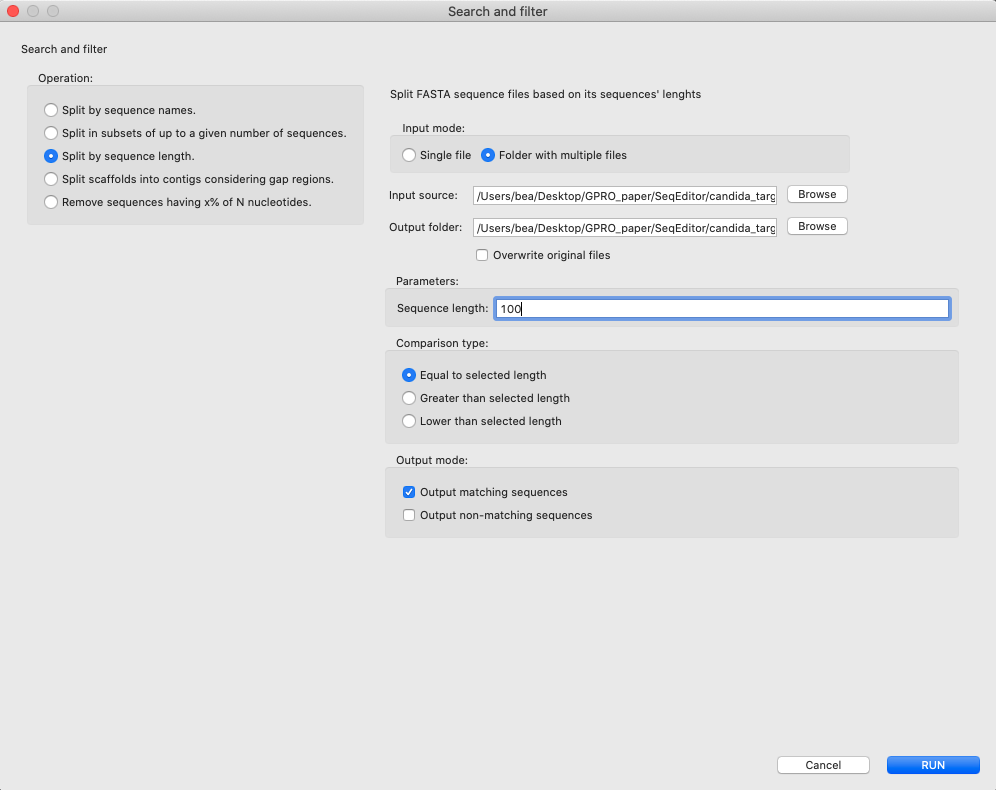
Figure 5: Split sequences dialog. The tool allows the user to: i) Split the sequences of your files by sequence names introducing list of names or a text file, including them in a select and match mode (exact or partial); ii) split in subsets of up to a given number of sequences introducing the number of sequences per file; iii) Split by sequence length introducing the desired length and select the comparison type: equal to selected length, greater than selected length or lower than selected length; iv) split scaffolds into contigs considering gap regions introducing sequence size and, if it is the case, a padding value.
[ Sequences → Remove/mask sequences ]:Removes or masks sequences having a certain percentage of a specific nucleotide or motif.
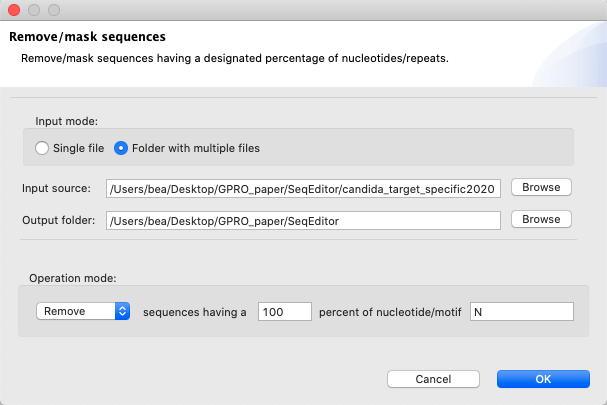
Figure 6: Remove/masks sequences from your fasta files. Using this parameter, the function will remove every sequence which is composed by a 100% of N.
TOP MENU: ORFs:
[ ORFs → Find ORFs in fasta files ]: Simultaneously searches and finds ORFs in one or more fasta files with multiple sequences.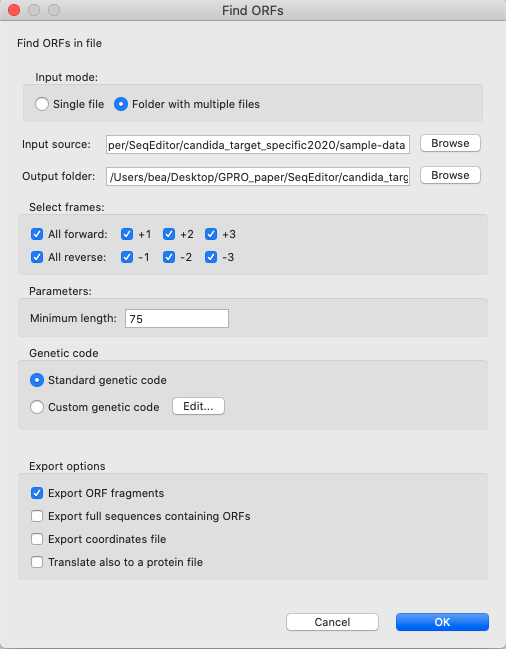
Figure 7: “Find ORFs” searches and finds ORFs, simultaneously, in one or more fasta files with multiple sequences just specifying a minimum length and the open reading frames (both forward and reverse). Detected ORFs can be selected and exported or translated and exported as protein sequences. The tool also exports annotation files with the coordinates of the ORFs.
[ ORFs → Translate nucleotide sequences in fasta files to proteins ]: Simultaneously translates to proteins all sequences contained in the fasta files.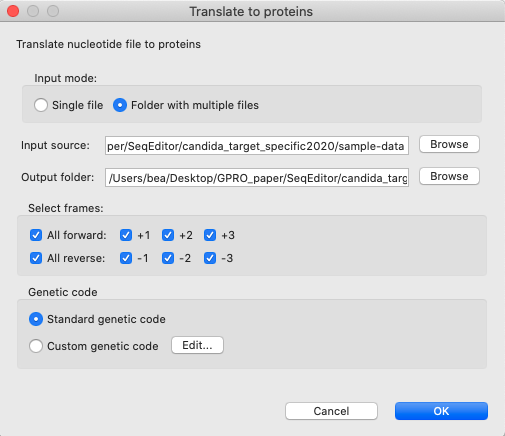
Figure 8: Translate to proteins dialog. Sequences contained in the fasta file can be translated into proteins by selecting the desired frame and genetic code. The output is a results file that contains the correspondent protein sequences obtained from each selected frame.
TOP MENU: MOTIFS
[ Motifs → Sequence motifs in fasta files ]: Simultaneously searches and finds sequence motifs in all the sequences contained in the fasta files.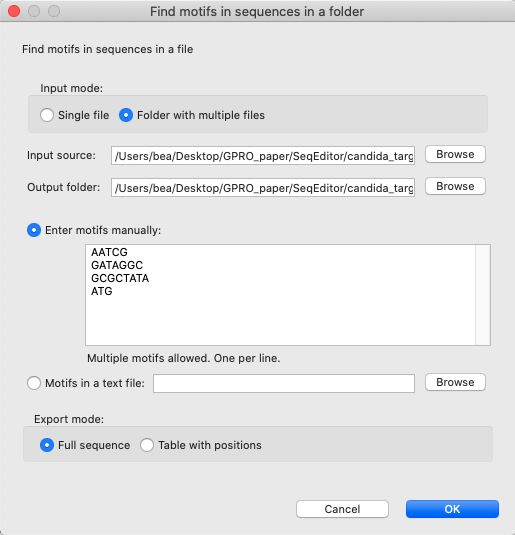
Figure 9: “Find motifs in sequences in a folder” dialog. By either introducing the motifs that need to be searched for either manually (one in each line) or by uploading them in a text file with the same format, this tool automatically searches for and finds these motifs in the selected fasta files.
TOP MENU: STATISTICS
[ Statistics → Infer sequence sizes in fasta files ]: Simultaneously infers the size of all sequences contained in the selected fasta files.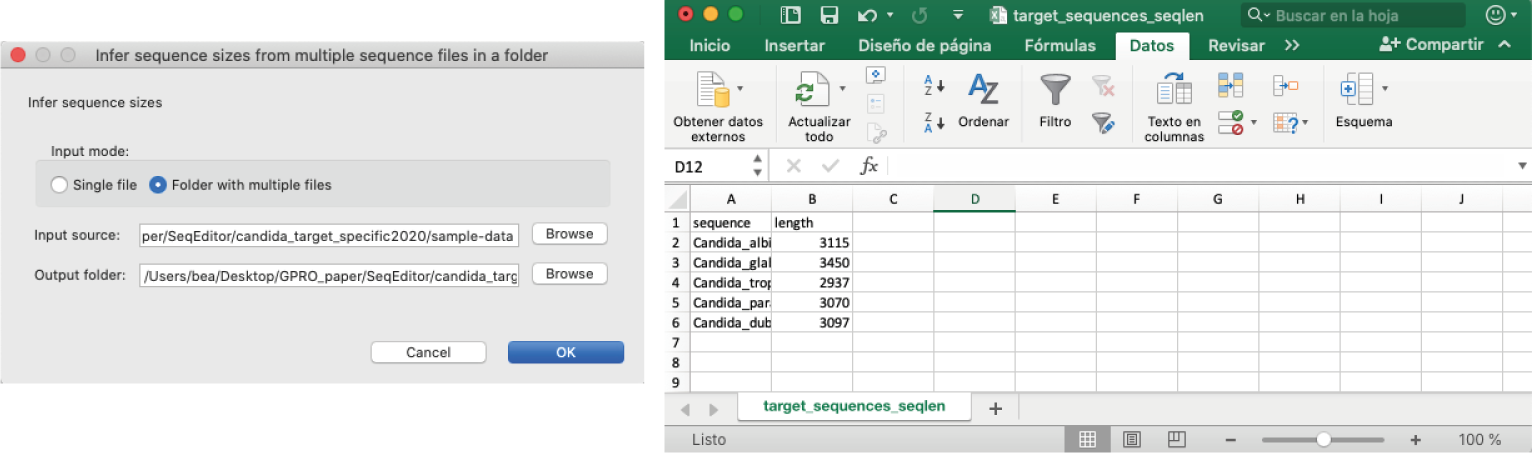
Figure 10: Infer sequence size tool: Left) Infer sequence sizes dialog; Right) Example of results file, containing the ID of the sequences and their correspondent length
[ Statistics → Infer overall metrics in nucleotide fasta files ]: Registers a given set of metrics from the sequences contained in the fasta files, namely the number of sequences as well as the size of the largest and shortest sequence, N50 and L50 using a Java implementation of the Assemblathon Stats script (Bradnam 2011). This option is only available for nucleotide sequences. 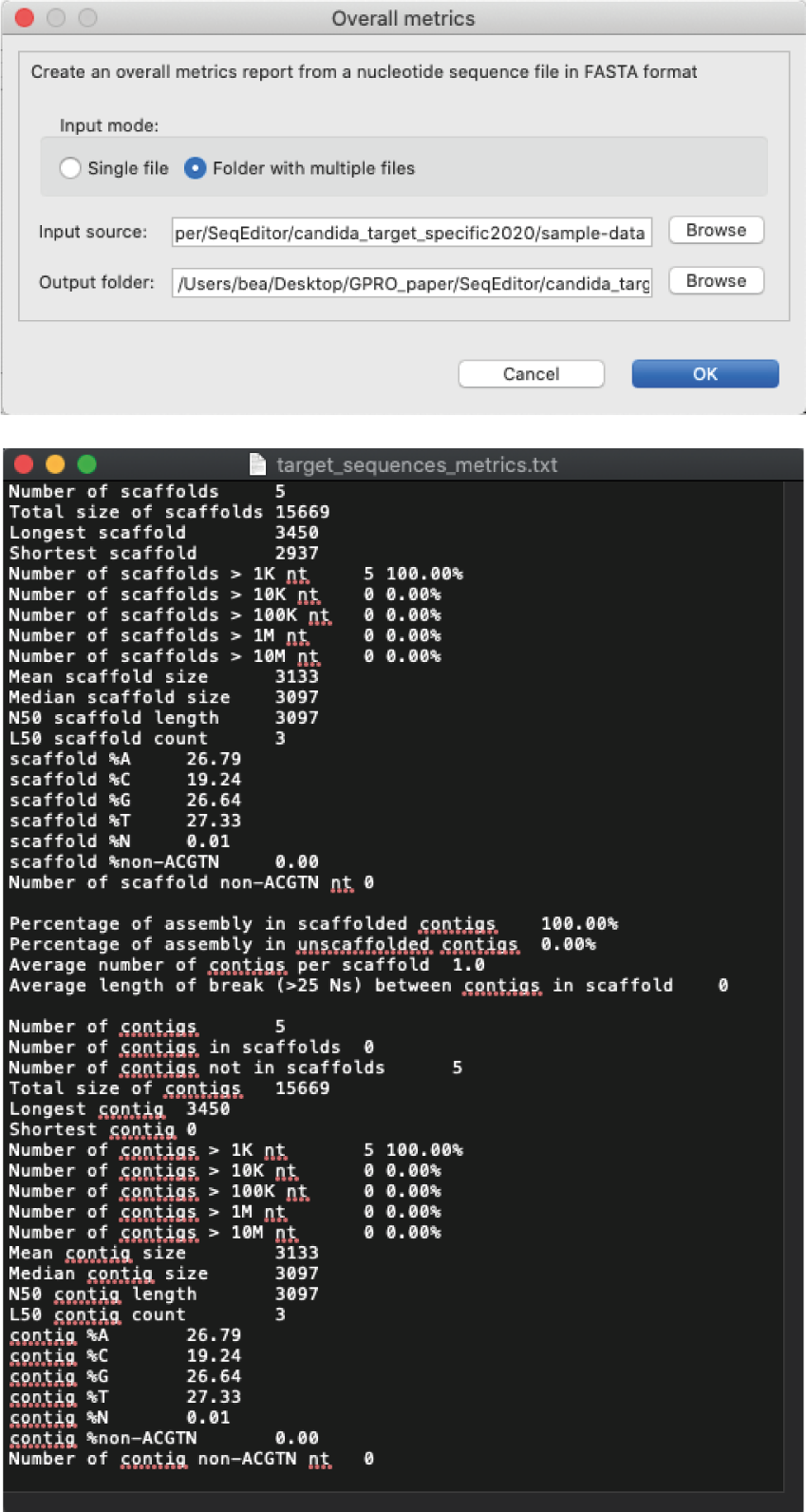
Figure 11: Sequence metrics inference dialog: Above) “Overall metrics” dialog: Below) Typical text file example of results obtained from this search, listing numbers of scaffolds/contigs, largest size found, N50 and L50 among others.
HELP:
[ Help → Manual ]: A link to this manual.[ Help → About SeqEditor ]: Other technical details and copyrigth of SeqEditor.
Figure 12: Sequence Browser Menu.
BROWSER MENU : Sequences
[ Sequences → Add New sequence ]: To create a new nucleotide/protein sequence.[ Sequences → Delete selected sequence ]: To selected sequences in the sequence browser.[ Sequences → Prints ]: To print the browsed sequence.[ Sequences → sort ]: Sorts options for multi-sequence files (only available when uploading a multi sequence file).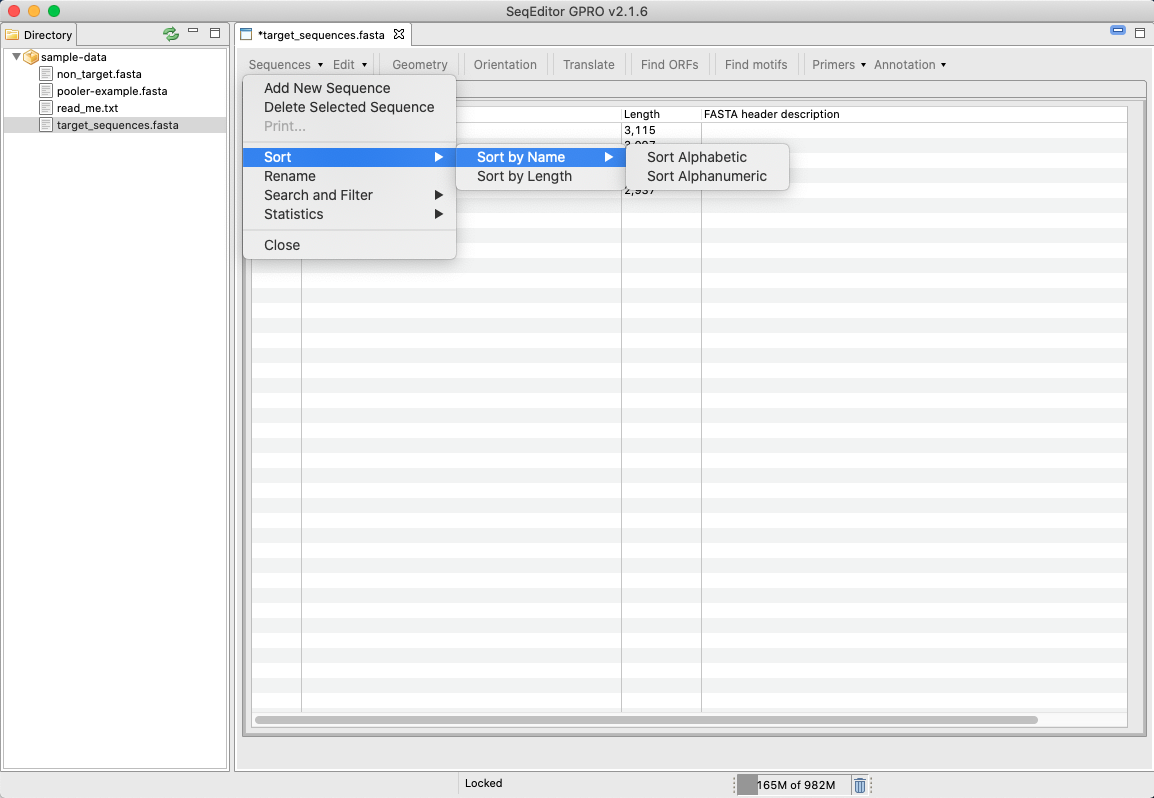
Figure 13: Sort sequences tool of the sequence browser menu. Using this option, the user can sort either by length or by name the sequences of a multiple fasta file opened in SeqEditor. The sequences will be listed either alphabetically or alphanumerically.
[ Sequences → rename ]: Allows the renaming of a selected sequence name[ Sequences → Search and Filter ]: Allows for the searching and filtering the sequences contained in the input file.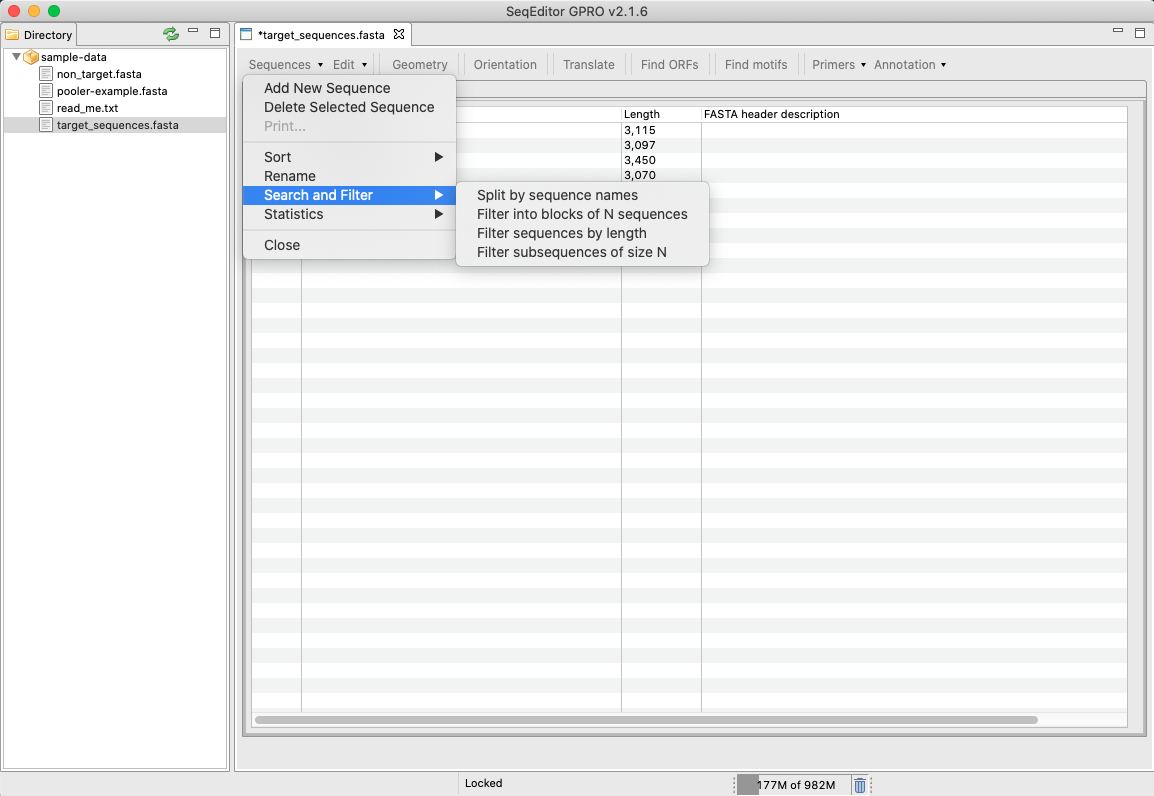
Figure 14: Search and filter option of the sequence browser menu. i) The “split by sequence names” option allows the user to split the sequence file into other files sorted by sequences names that are selected by the user. These names can either be inputted via a text file or manually in the dialog, selecting a matching mode (exact or partial.; ii) The “split into blocks of N sequences” option allows the users to do so by introducing the number of sequences per file. iii)The “filter sequences by length” option does so when introducing the sequence length and the comparison of choice (equal, greater than or lower than). iv) The “filter subsequences of size N splits at gap regions, if present, by selecting the sequence size and a padding value when applicable.
[ Sequences → Statistics ]: Displays the overall metrics of the sequences contained in the selected fasta file as shown in Figure 11BROWSER MENU : EDIT
[ Edit → Undo ]: To undo a edit made on the sequence.[ Edit → Redo ]: To redo a edit made on the sequence.[ Edit → Cut ]: To cut a sequence from the sequence browser.[ Edit → Copy ]: To copy a sequence from the sequence browser.[ Edit → Paste ]: To paste a sequence in the sequence browser.[ Edit → Locked ]: To lock/unlock the sequence if you want to make edits on it.BROWSER MENU : GEOMETRY
[ Geometry ]: It allows the change from DNA to RNA and vice versa, as well as the view of the sequence as a single or double strand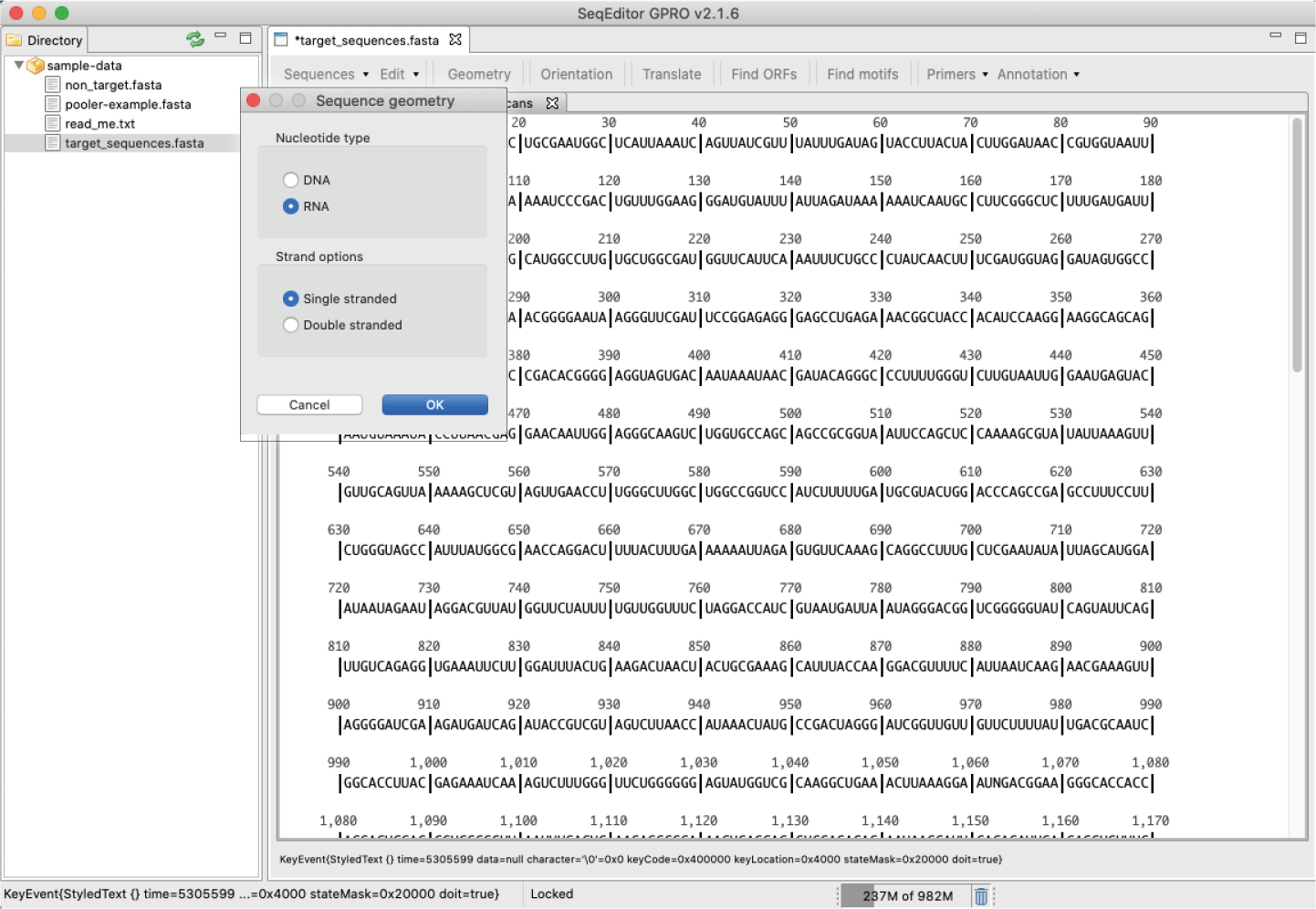
Figure 15: Changing the geometry of a sequence via the “Geometry” option in the sequence browser menu: Left) Sequence geometry selection dialog; Right) Example of change in geometry from double stranded DNA to single stranded RNA
BROWSER MENU : ORIENTATION
[ Orientation ]: Switches the sequence orientation as 1) reverse, 2) complementary or 3) reverse-complementary.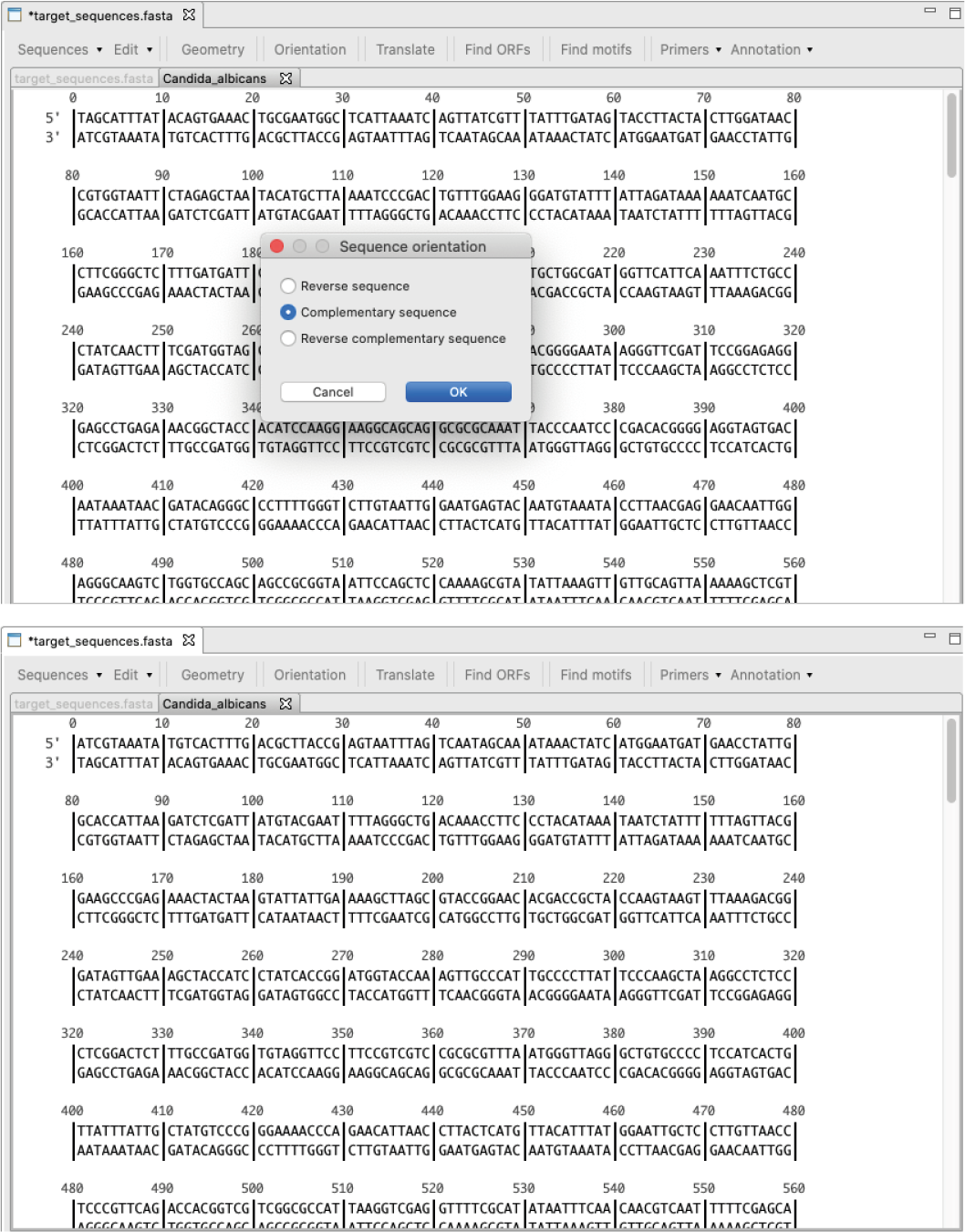
Figure 16: Changing the orientation of a sequence: Above) Orientation dialog to change to reverse, complementary or reverse complementary sequence; Below) sequence with the orientation changed to the complementary sequence.
BROWSER MENU : TRANSLATE
[ Translate ]: Translates nucleotide sequences into proteins by selecting the desired frame(s) – on the forward or reverse strand starting from the +1, +2 or +3 nucleotide positions. Either the standard genetic code or a custom one can be selected for reference. The translate tool can open Gene Runner’s translation table format (.trt files) as well as a native plain text format files (.txt), which can be created in any text editor of choice. Please note that in these files, lines that start with the hash symbol (“#”) are interpreted as comments and thus will be ignored (with the one exception of the first line that will hold the code’s name. However, this line is not mandatory). Each following line is composed of a codon (RNA and DNA are allowed), a hyphen and a ‘greater than’ symbol (“>”) followed by the correspondent amino acid symbol according to the 1-letter IUPAC code.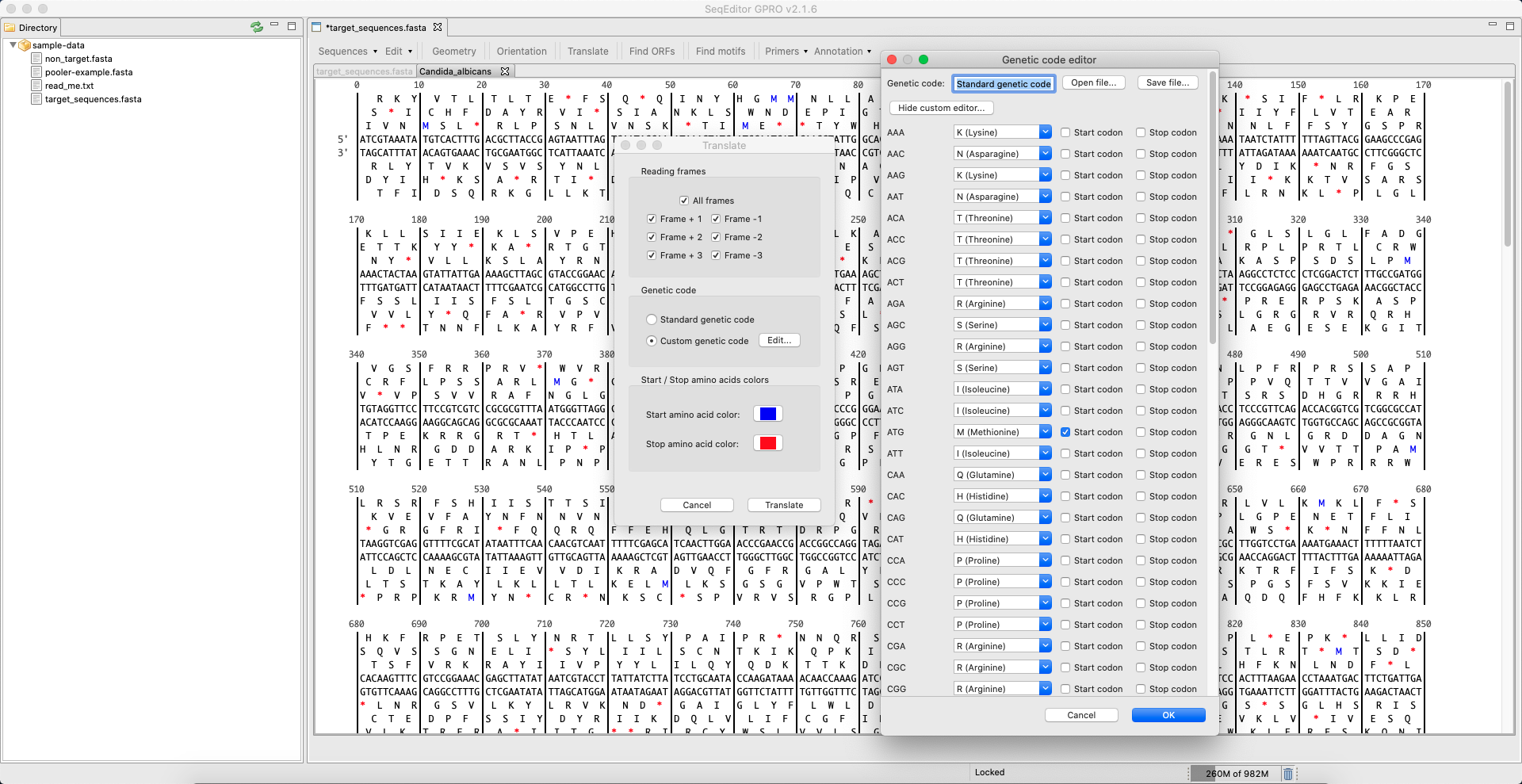
Figure 17: “Translate” dialog and Genetic code editor dialog. The tool calls a pop-up dialog allowing users to translate nucleotide sequences into proteins by selecting the desired translation frame (+1, +2, +3). The standard genetic code is used by default. However, a custom genetic code can also be selected. Once translated, codons can be edited, renamed and saved. Previously saved custom codes can also be opened. The default colors for the start and stop codons are set in blue and red respectively but can be changed using the color palette in the dialog.
BROWSER MENU : FIND ORFs
[ Find ORFs ]: Searches and retrieves ORFs contained both the forward and the reverse strands by specifying a minimum ORF length. 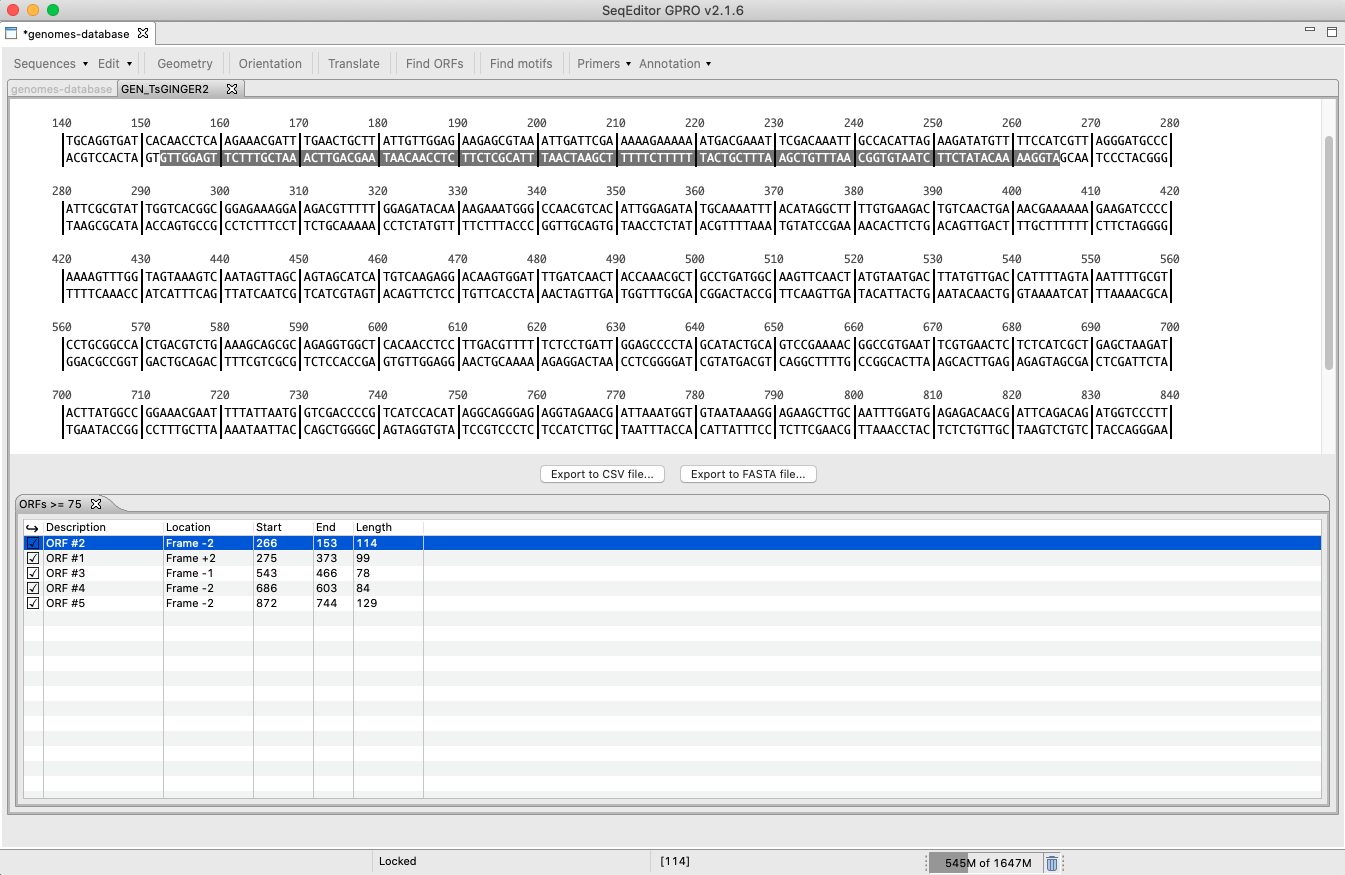
Figure 18: Find ORFs tool. By selecting a length of the ORF, a search is performed and the corresponding report is produced listing the found ORFs. ORF coordinates are specified on the summary browser. By clicking on a given ORF, it will be selected and highlighted in the Sequence Browser. Results can be then exported as sequences or annotations. In the first case, the tool will allow the sequence to be exported as either a nucleotide or a protein sequence.
BROWSER MENU : FIND MOTIFs
[ Find Motifs ]: This option performs searches for a specific protein or nucleotide motif (binding sited, restriction sites, etc.). Once the search is completed, results will be shown in the summary browser. You are also allowed to search for multiple motifs as single occurrences or as clusters of motifs by accessing the “Multiple Motif Editor” located in the “Find motif” interface. 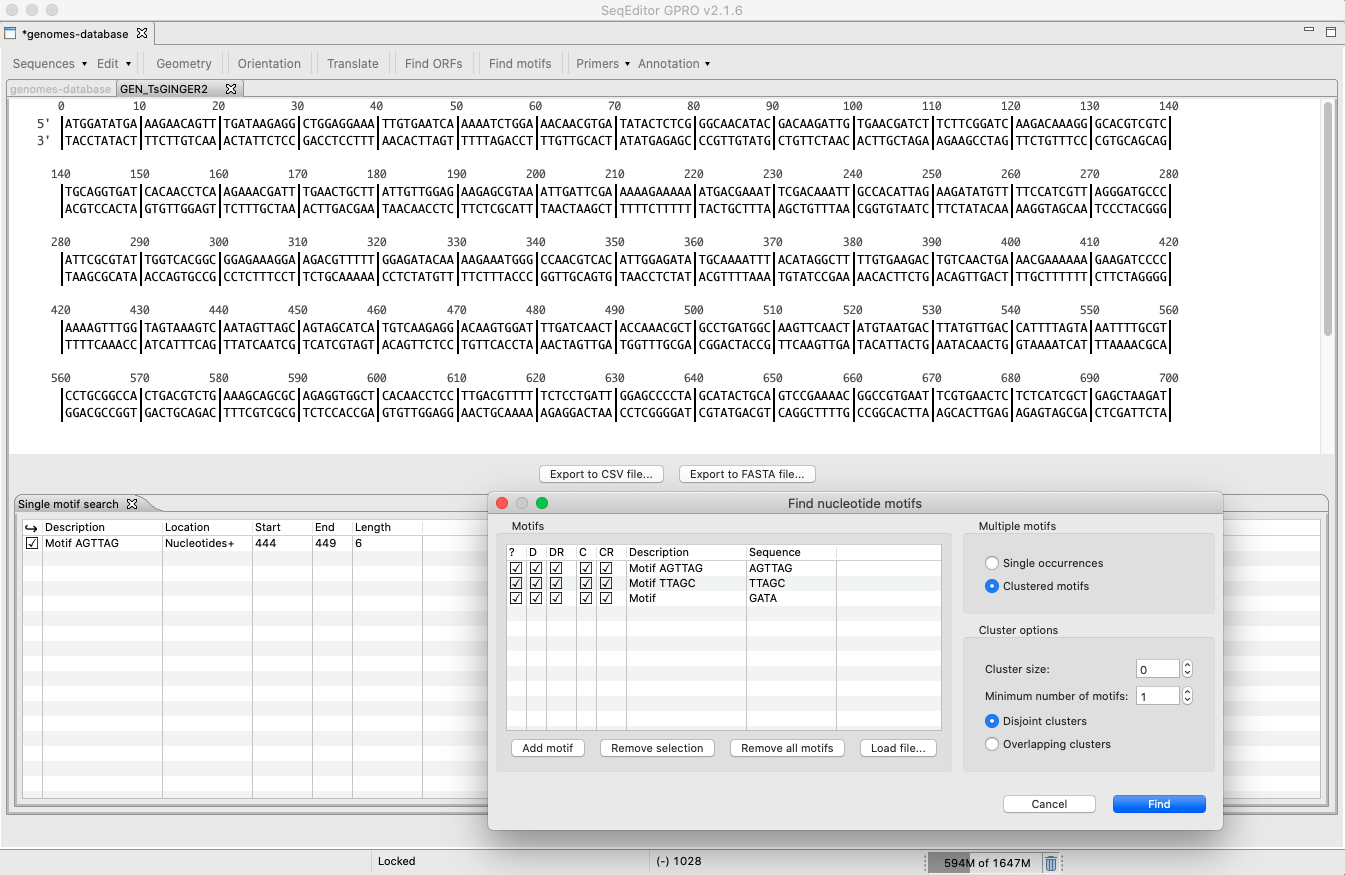
Figure 19: Multiple Motif Editor dialog. The search for motifs can be performed either as single occurrences if the motifs are searched as independent terms or as clustered motifs withmotifs falling together in a sequence frame. In that case, some search parameters will need to be selected, namely i) Minimum cluster size (for instance, a frame of 500 nucleotides); ii) Minimum number of motifs within the cluster; iii) Select whether clusters are allowed to overlap (overlapping clusters option) or not (disjoint clusters option). Note that you can also add motifs from a file using the tab “Load File” in the Multiple Motif Editor.
BROWSER MENU : Primers:
SeqEditor implements a set of three tools for singleplex, multiplex PCR primer design and primer pooling powered by an interface adaptation of two CLI tools: Primer3 (Untergasser et al. 2012) and PrimerPooler (Untergasser et al. 2012). This tool also incorporated a newly optimized search process that is based on two algorithms for multiplex and target-specific primer design (Hafez et al. 2020). These three tools (designated as SinglePlexPCR, MultiPlexPCR and PrimerPooler respectively) are organized in three separate interactive interfaces that are accessible through the “Primers” tab of the browser menu.[ SinglePlex Primers ]: Searches for primers for the amplification of one or more sequences. This option can be run in two modes:
Batch run mode: searches for primers suitable for all sequences contained in a given file
Single run mode: searches for primers that are suitable for a given sequence that has been opened only
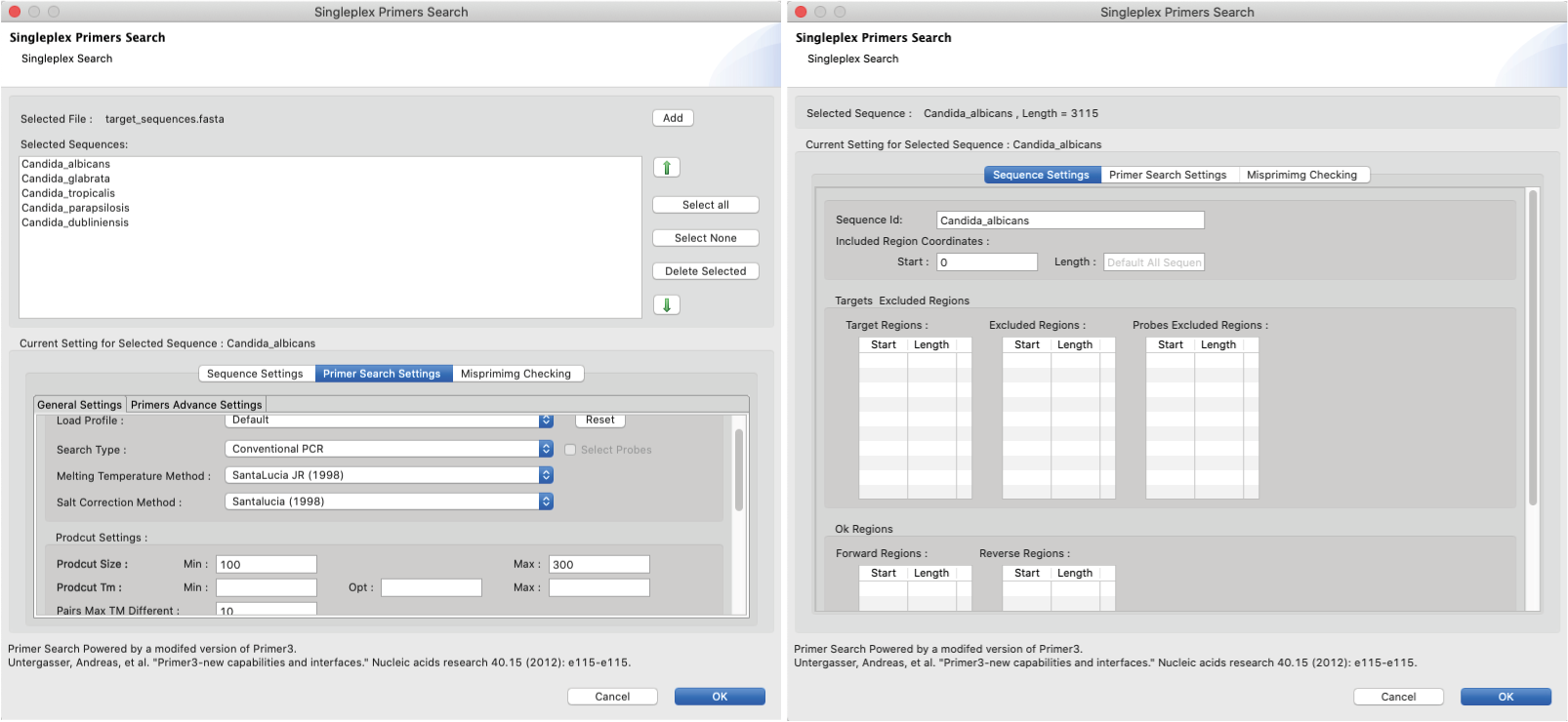
Figure 20: Singleplex Primer Search dialogs: Lef) SinglePlex primer search in batch mode. The file upload window is displayed at the top; Right) SinglePlex primer search in single mode. Once this mode has been selected the search parameters can be set at the bottom panel. There are three main tabs to enable this: i) Sequence setting: The ‘sequence ID’ for which primer search will be launched on can be inputted here. Once the search has been performed, the bottom panel will display those regions that correspond to on target, off target (excluded), and probe excluded regions obtained in the search. ii) Primer Search Settings: allows the following search parameters to be set: 1) general settings such as primer length, Tm,GC content and product size; 2) Advanced settings such as thermodynamic calculations and other primer and score calculation settings; 3) Advanced settings -similar to the advanced primer settings- but to be applied for probes only; iii) Mispriming Cheking: Allows the user to input a library of mispriming sequences to be used during the search
[ MultiPlex Primers ]: It allows the search of MultiPlex and species-specific primers for multiple target sequences using different settings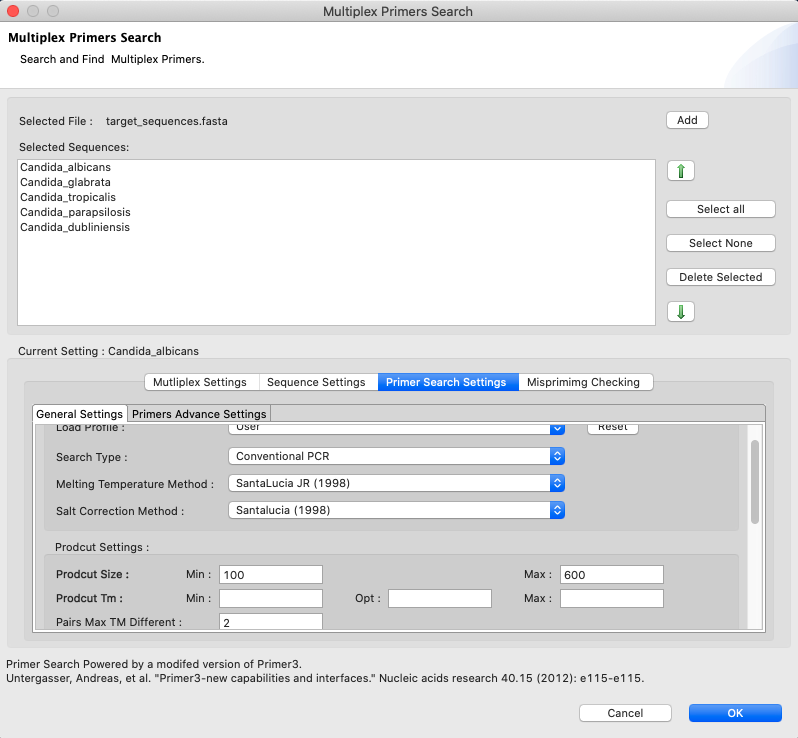
Figure 21: Multiplex Primer Search dialog. The search parameters can be set through four main tabs displayed at the bottom, namely ‘Sequence Settings’, ‘Primer Search Settings’, ‘Mispriming Settings’ and ‘Multiplex Settings’. The first three are identical to those included in the SinglePlex Primer Search and their parameters are described in Figure 20. Multiplex Settings allows the user to assign a name for the group search.
[ PrimerPooler ]: Optimizes the multiplex PCR input by dividing the primers into different pools. 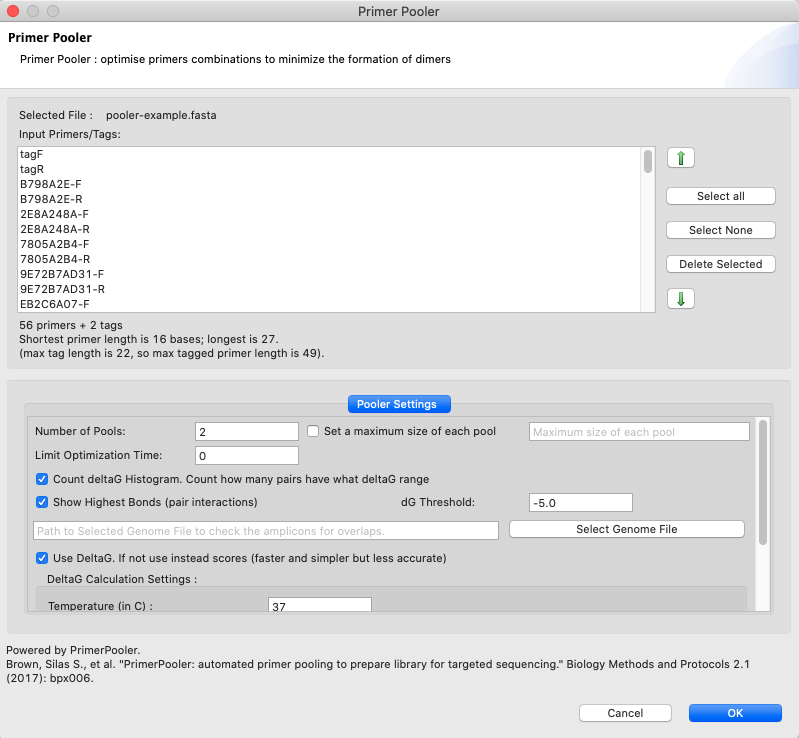
Figure 22: PrimerPooler tool dialog. The following parameters can be set when using this tool: i) Number of pools to divide the input into (“Number of pools” option); ii) Setting a maximum size for each pool to make the pools more even (“Set max Size of Pools”); iii)Creating histograms from the deltaG/Score for all pairwise interactions of all primers (“Count deltaG/Score”); iv)Showing a summary and the dimer structure formed from the pairwise interaction with the highest interaction (“Show Highest Interaction”); v) Selecting a genome file in 2bit format to check the amplicons for overlaps (Select Genome) Primer pairs that amplify overlapping regions of the genomes can produce an unwanted shorter amplicon if used in the same pool; vi)Use thermodynamic principles to calculate the correspondent ∆G for the pairwise interaction (Use DeltaG). If not selected, a score will be automatically calculated based on alignment. However please note that such a score will be calculated in a faster yet less accurate way. To use deltaG additional parameters such as temperature, concentration of magnesium, concentration of monovalent cation and concentration of deoxynucleotide (dNTP) will need to be inputted.
BROWSER MENU: Annotation
SeqEditor supports the analysis of genomes and transcriptomes that have a reference annotation file (GTF/GFF). Thus, we have incorporated a GTF/GFF viewer that reads the reference annotation file allowing the users to search, filter, and extract sequence features (such as chromosomes, genes, exons or introns) contained in the assembly file using the annotation as a reference.[ Open Annotation File ]: Opens and attaches the annotation file (GTF/GFF) to the previously opened fasta file.[ View/Hide ]: Views/hides the annotation viewer.[ Close Annotation Set ]: Closes/saves the opened annotation file.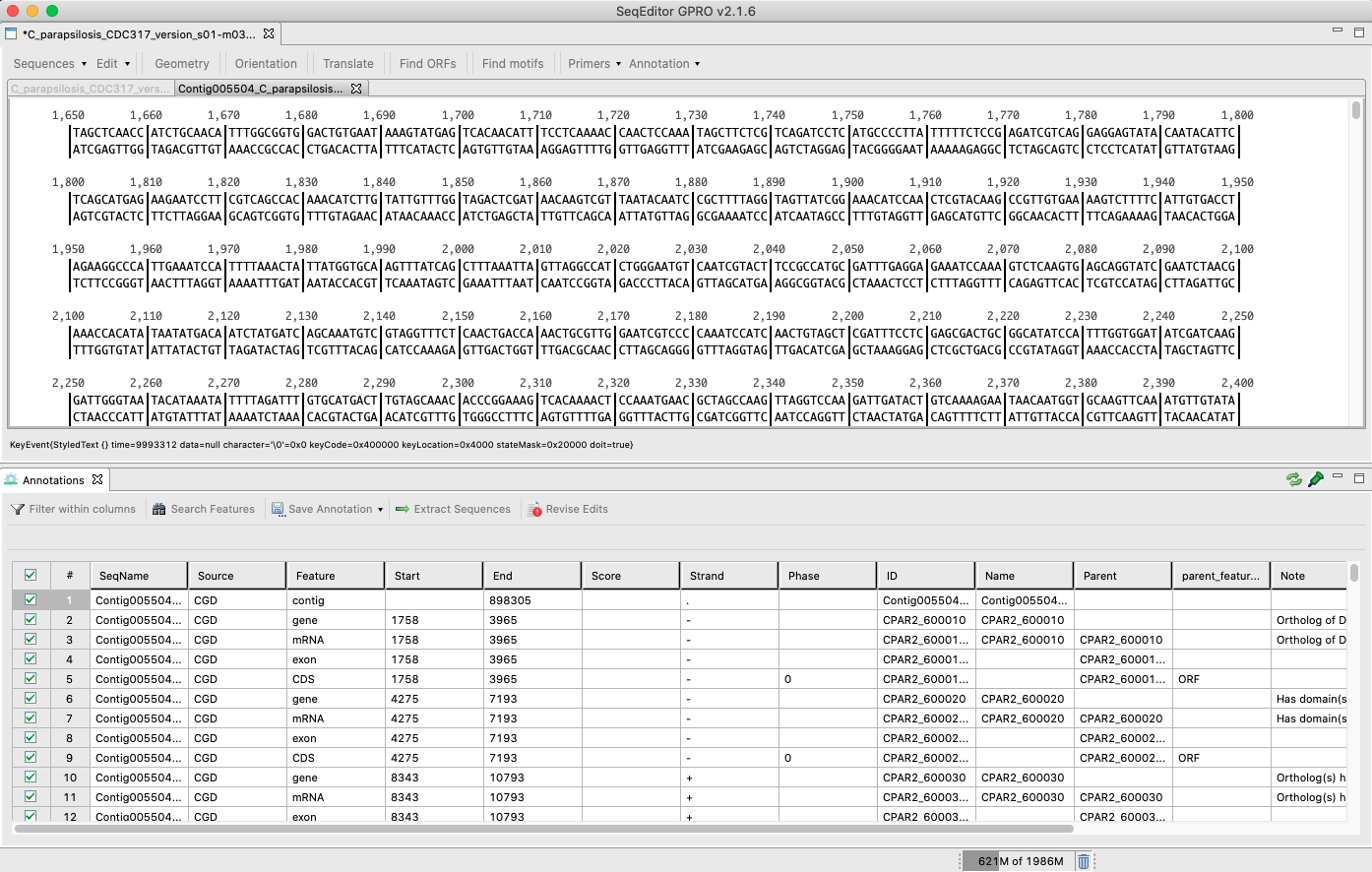
Figure 23: View of the sequence browser (top) and the GTF/GFF viewer (bottom) when opened simultaneously. The annotation viewer shows the features (such as gene, exon, CDS, etc.) that are contained in the sequence of interest. The viewer has five additional options for the management of these annotations: i) Filter within columns: Shows/hides the filter option. When the filter option is shown, the user can filter by any of the terms contained in any column displayed in the annotation file. For example, when writing “gene” on the filter section of the Feature column, the annotation viewer will only display those rows that correspond to a gene. ii) Search Features: Searches and checks a feature according to different criteria; III) Save Annotation: Saves, Saves As or Exports (just for rows); iv) Extract sequences: Extract features from the reference sequences through a pop-up dialog; v) Revise Edits: Revises and corrects the features of the coordinates that are affected by the edition of the reference sequence.
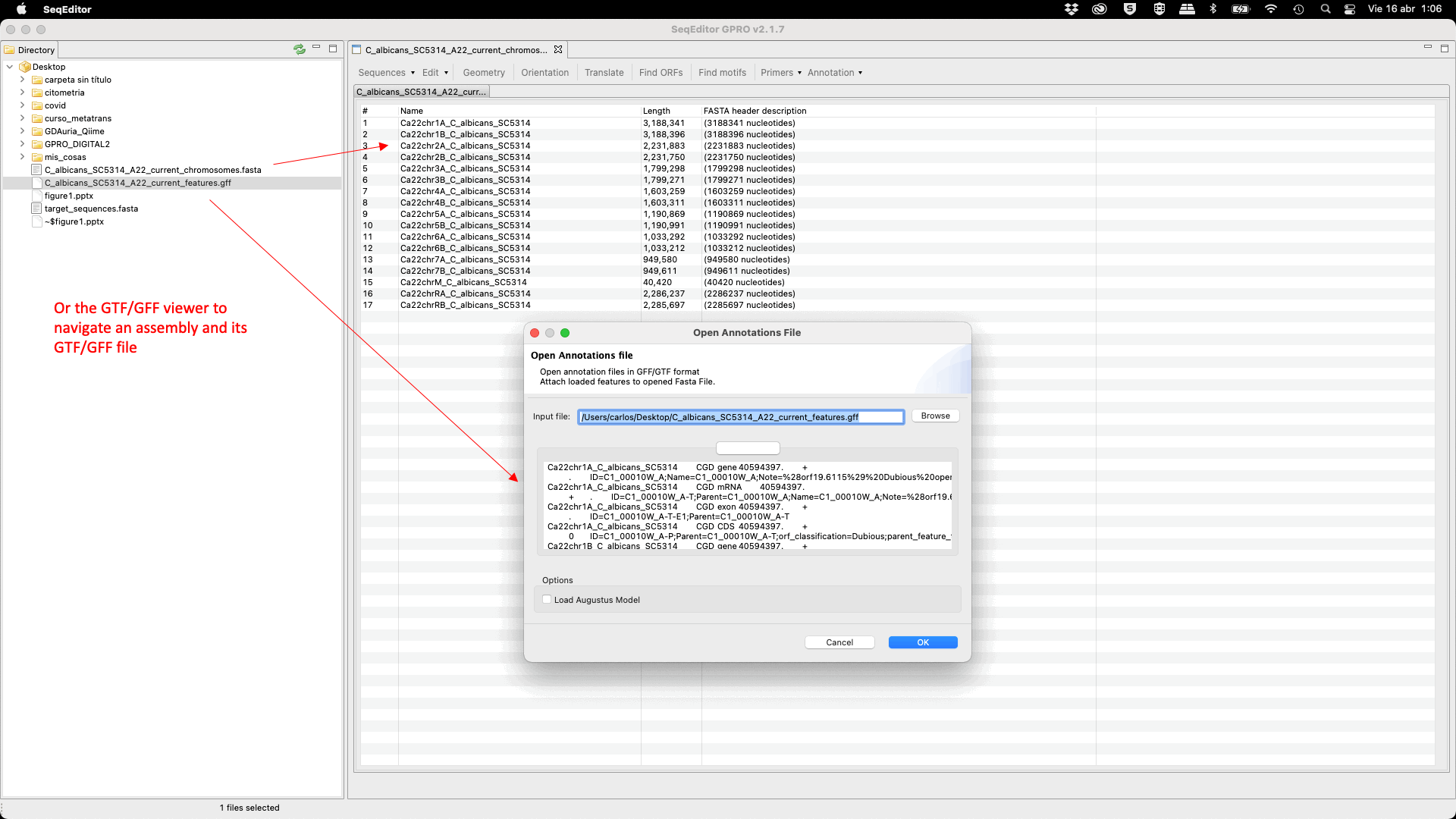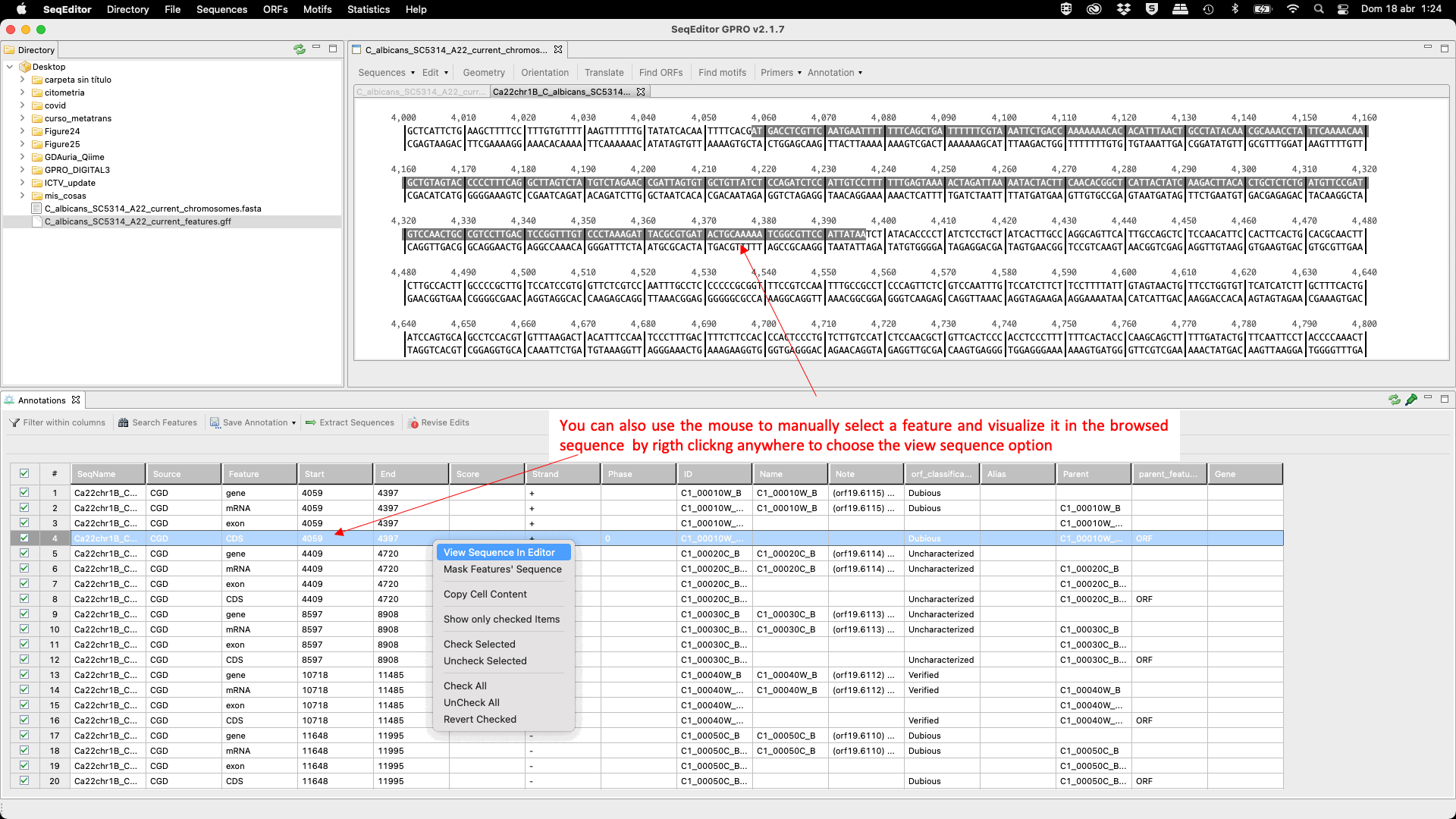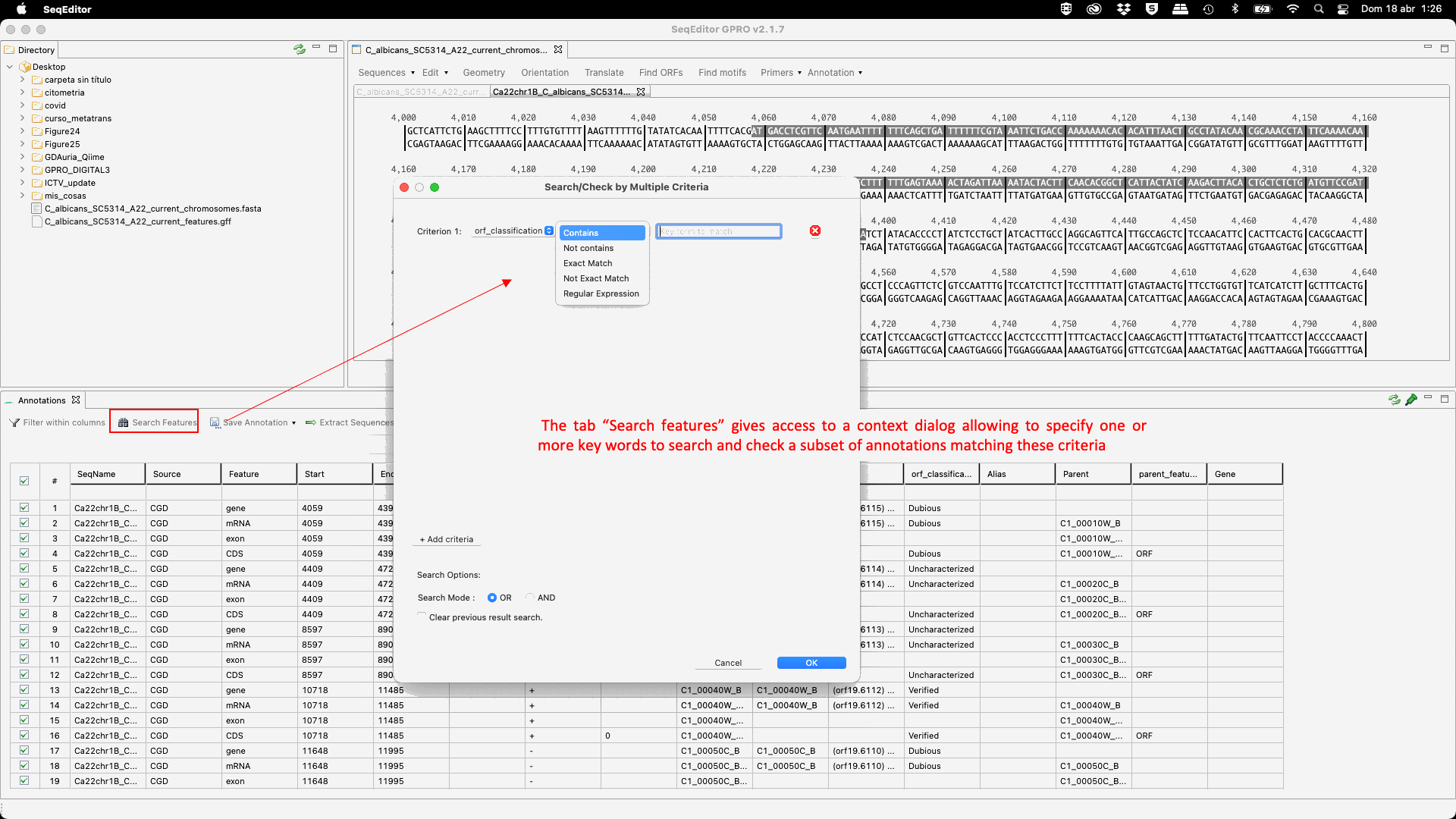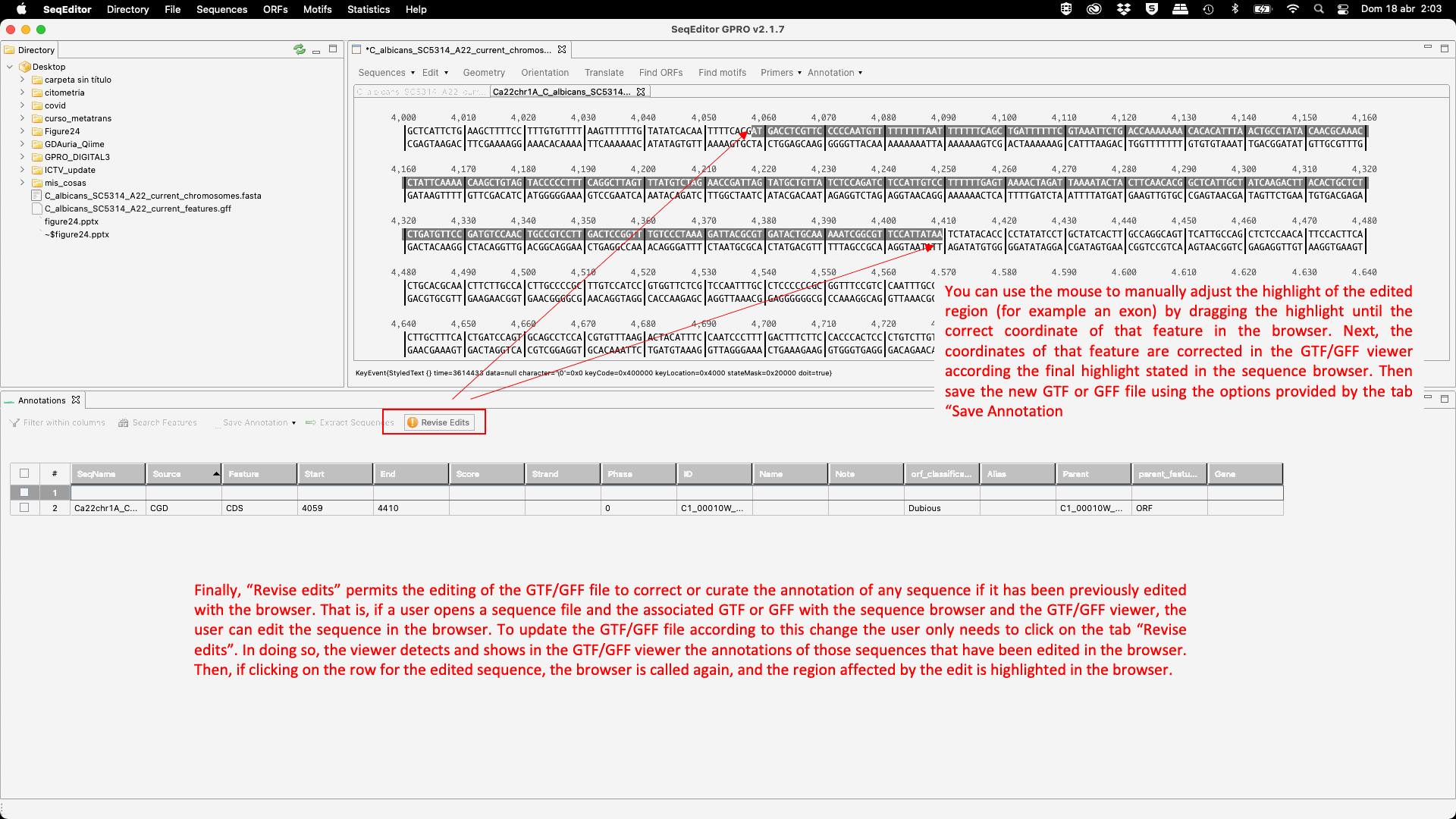
Figure 24: GTF/GFF viewer: mouse-dependent and menu options.





